Investigating the relationship between the summer northernmost position of southerly wind and precipitation over East China
Date:2014-12-12
The relationship between the summer northernmost position of southerly wind and precipitation over East China is investigated. The northern limit of summer southerly wind index (NLSSWI) over East China is defined as the latitude where the longitude-averaged (105–120°E) low-level meridional wind is equal to zero. Results show that there is a significant negative (positive) correlation between NLSSWI and summer precipitation over the Yangtze River (North China) region. Thus, the proposed NLSSWI may have implications for the prediction of summer precipitation anomalies in these regions. In positive NLSSW index years, a cyclonic circulation anomaly is observed over the tropical western North Pacific and an anticyclonic circulation anomaly is seen over the subtropics of East China, accompanied by southerly anomalies over East China. This leads to above-normal moisture penetrating into the northern part of East China. In addition, significant upward (downward) motion anomalies can be found over the North China (Yangtze River) region. As a result, there are significant positive (negative) precipitation anomalies over the North China (Yangtze River) region. Further examination shows that sea surface temperature anomalies over the tropical eastern Pacific and Indian Ocean both contribute to the formation of NLSSWI-related circulation anomalies over the tropical western North Pacific.
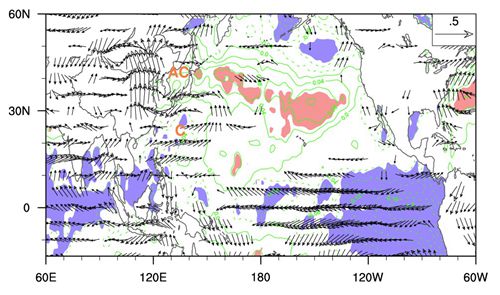
Anomalies of JJA SST (contours) and winds at 850 hPa (vectors) regressed on the NLSSWI during 1958–2001. Red (Blue) shading denotes positive (negative) SST anomalies that are significantly different from zero at the 95% confidence level. Contour interval is 0.04°C. The wind vector scale is shown in the top-right corner (units: m s?1).
Citation: Mei, S.-L., W. Chen, and S.-F. Chen, 2015: On the relationship between the northern limit of southerly wind and summer precipitation over East China, Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 8, 000–000, doi:10.3878/AOSL20140078.
