The relationship between the interdecadal variation of summer precipitation and its interannual variability over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Valley
Date:2015-02-05
The relationship between the interdecadal change in the intensity of summer precipitation and its interannual variability over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Valley (MLYRV) is investigated, by analyzing five gauged and re-constructed precipitation datasets. The relationship is found to be very weak over the MLYRV, with a correlation coefficient of only approximately 0.10. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation influences the western North Pacific subtropical high, which is responsible for the interdecadal change in summer precipitation over the MLYRV. However, the precipitation interannual variability is closely related to the ENSO events in the preceding winter due to its impact on the meridional displacement of the East Asian westerly jet. Different physical mechanisms cause different interdecadal variations, and thus result in a poor relationship.
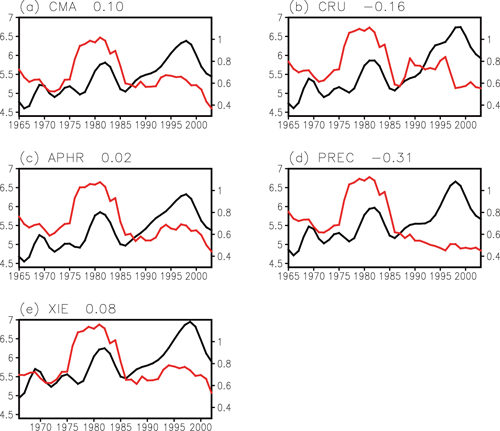
Interdecadal variation of the summer precipitation (black line, left ordinate) and nine-year window slipping interannual StD (red line, right ordinate) over the MLYRV, and the correlation coefficients. Unit: mm/day.
Citation: Fu, Y.-H., 2015: The relationship between the interdecadal variation of summer precipitation and its interannual variability over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Valley. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 8, doi:10.3878/AOSL20140098.
Download: http://159.226.119.58/aosl/EN/abstract/abstract536.shtml#
