IAP Scientists Explained Warmer Climate in the Tang and Song Dynasties
Date:2015-03-04
Chinese are generally proud of Tang dynasty (618?907 AD) which was considered a golden age

City Wall of Xi'an, once the capital of Tang Dynasty, also the starting point of the Silk Road (photo from Wikipedia)
From a perspective of natural science, a paleoclimate research team from Nansen-Zhu international research center at Institute of Atmospheric Physics investigated possible mechanisms for the warming over China during the Tang and Song dynasties. They performed a 2000-year simulation forced by the external forcings of the last two millennia with the Community Earth System Model. The simulation indicates warm conditions in both the early Tang dynasty (650?700 AD) and early Song dynasty (950?1000 AD), but the warmth is mainly seen in East China in the early Tang dynasty, and over the whole of China in the early Song dynasty. The warming in the early Tang dynasty is attributed to the localized increase of atmospheric net energy with favorable heat transport, whereas results from the increase of global solar radiation in the early Song dynasty. Based on the simulation and reconstructions, they suggest that the early Tang dynasty warm period may have been a regional phenomenon in China, while the early Song dynasty warm period was a reflection of global/hemispheric-scale warm events that took place at the same time.
The results are published in Journal of Geophysical Research.
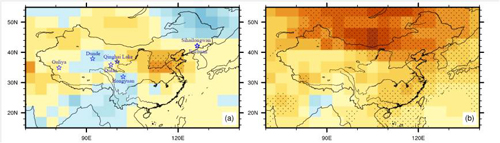
Annual mean temperature anomalies (°C) in the early Tang dynasty warm period (650-700 AD; a) and the early Song dynasty warm period (950-1000 AD; b).
Citation: Q. Yan, Z. Zhang, H. Wang and D. Jiang, 2015: Simulated warm periods of climate over China during the last two millennia: The Sui-Tang warm period versus the Song-Yuan warm period, Journal of Geophysical Research, doi:10.1002/2014JD022941
Download: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014JD022941/abstract
Contact: YAN Qing, yanqing@mail.iap.ac.cn
