Projected climate change against natural internal variability over China
Date:2015-03-24
The ability of 42 Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) models in simulating the annual and seasonal temperature and precipitation over China is first examined by using their historical experiments for 1986–2005, and then 39 relatively reliable models are chosen to project temperature and precipitation changes against the natural internal variability over the country under the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) scenarios in the 21st century. The result shows the temperature continuing to increase, especially in northern China. The annual warming for 2081–2099 relative to 1986–2005 over the whole of the country is larger than the background variability, with the multi-model median changes under RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6.0, and RCP8.5 being 9.9, 19.3, 22.8, and 35.9 times greater than one standard deviation of internal variability, respectively. The annual precipitation is projected to increase by 6.1%, 9.3%, 9.6%, and 16.2% for 2081–2099 relative to 1986–2005 under RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6.0, and RCP8.5 respectively, while large changes with high model agreement only occur over the northern Tibetan Plateau and Northeast China, which is mainly due to the robust changes in winter and spring under RCP6.0 and RCP8.5.
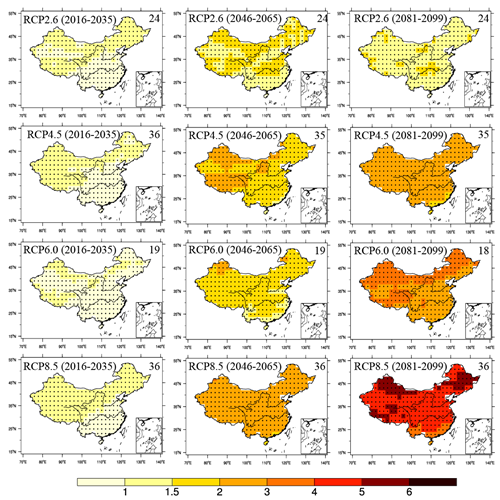
Figure 1 Multi-model median of annual temperature changes (units: °C) relative to 1986–2005 for 2016–2035, 2046–2065, and 2081–2099 under RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6.0, and RCP8.5, respectively. Stippling indicates regions where the median change is greater than two standard deviations of internal variability and where at least 90% of models agree on the sign of change. Blank space indicates regions where the median change is between one and two standard deviations of internal variability. The number in the top-right corner indicates how many chosen models were available.
Citation: Jiang, J., Y. Sui, and X.-M. Lang, 2015: Projected climate change against natural internal variability over China, Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 8,doi:10.3878/AOSL20140096.
Link: http://159.226.119.58/aosl/EN/abstract/abstract548.shtml
