Impact of the North Atlantic SST Tripole Pattern on the Spring Atmospheric Heat Source over the Tibet Plateau
Date:2015-09-17
A recent work from Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP), Chinese Academy of Science indicated that the remote ocean forcing over the North Atlantic can modulate the interannual variability of the spring atmospheric heat source over the TP.
The Tibetan Plateau (TP) is situated in the Asian subtropical region. The role of the TP thermal forcing in modulating the large-scale atmospheric circulation and Asian Monsoon has been well documented, whereas the impact factors contributing to the variability of the in situ atmospheric heat source receives much less attentions. By employing data diagnosis and numerical simulations, Dr. CUI Yangfan and her colleagues from IAP found that the positive phase of North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) in JFM (January-February-March) can trigger a tripole pattern of sea surface temperature in North Atlantic. Such a tripole pattern can persist until FMA (February-March-April). The warm core of the tripole pattern stimulates a steady atmospheric Rossby wave train to the downstream region, which further intensifies the spring west jet over the TP and hence the enhanced surface sensible heating and even the total atmospheric heat source. As a result, the forthcoming East Asian summer monsoon will be intensified as well.
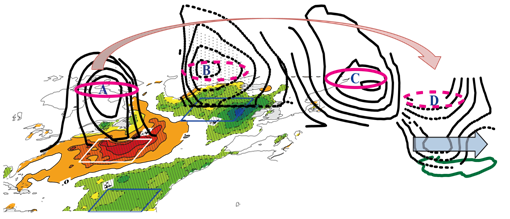
The warm core of the tripole pattern of sea surface temperature (red shaded areas) over the North Atlantic stimulates a steady and equivalent barotropic downstream Rossby wave train (black line and red line), which further intensifies the spring west jet over the TP (green line).
They then proposed a mechanism to explain how the remote large-scale air-sea anomalies over the North Atlantic from winter to spring modulates the spring thermal forcing of the TP and the subsequent interannual variability of East Asian summer monsoon. The study was published in September 2015 in Climate Dynamics.
Citation: Cui YF and Duan A, Wu GX, Liu YM, 2015: Interannual variability of the spring atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau forced by the North Atlantic SSTA. Climate Dynamics (doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2417-9)
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-014-2417-9
Contact: Dr. DUAN Anmin, cuiyangfan@lasg.iap.ac.cn
