IAP Achieved New Understanding of Local Heavy Rainfall Events over the Beijing Metropolitan Region
Date:2016-11-18
The Beijing Metropolitan Region (BMR) often suffers from heavy rainfall events. The complex topography with the Yan Mountains to the north and the Taihang Mountains to the west, as well as the diverse underlying urban surfaces make the predictions of convective initiations (CIs) and local heavy rainfall events over the BMR much difficult. Especially, the CIs and consequent heavy rainfall events occurring under weak synoptic forcing are extremely great challenges to today’s operational NWP models and even experienced forecasters.
Recently, IAP researchers, LI Huiqi, CUI Xiaopeng and their co-authors (Prof. Da-Lin ZHANG from University of Maryland, associate professor ZHANG Wenlong from Institute of Urban Meteorology, and senior engineer QIAO Lin from Beijing Meteorological services) performed observational and modeling studies on two local heavy rainfall events over the BMR occurring under weak synoptic forcing. The CI processes were specially investigated.
Their results revealed that the cold pool outflows associated with precipitation systems around the BMR, the underlying urban surface and the local topography dominated where and when CIs and consequent heavy rainfall occurred. A sudden local heavy rainfall event produced by several scattered convective storms in 2008 interrupted the scheduled matches of the ongoing 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. The detailed observational analysis showed that small-scale topography and cold pool outflows were two key influencing factors in the development of the convective storms.
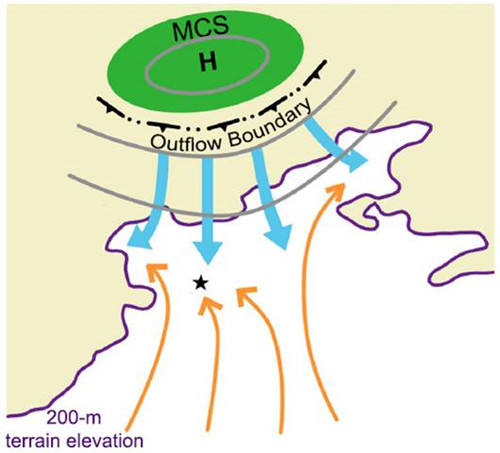
Figure 1 Schematic diagram for the CI of the Haidian storm on 9 August 2011. The star marks the CI location. Orange arrows indicate the surface southerly flow. Thick blue arrows indicate the northerly flow associated with a convectively generated meso-high depicted by grey contours. Yellow shadings denote the mountainous regions. (Image plotted by IAP)
As for another local heavy rainfall event over the BMR in 2011, an isolated convective storm was initiated suddenly over Haidian district of Beijing, far away from the outflow boundary associated with a precipitation system over the northwestern mountains. They revealed that the “northwestward-concaved valley” near Haidian and Changping districts and the urban surface accounted for the formation of a favorable convergence zone near the border of the above two districts, facilitating the confluence of high equivalent potential temperature air. The isolated convective outbreak would not be possible without the sustained low-level convergence of high equivalent potential temperature air between south- to southeasterly flows and a northerly flow. The latter occurred far ahead of the outflow boundary associated with a convectively generated cold pool by the northwestern precipitation system. Their studies revealed the mechanisms for the development of local storms and consequent heavy rain in the BMR, which have important implications for improving relative prediction skills.
The results were recently published in Atmospheric Science Letters and Monthly Weather Review.
References:
Huiqi Li, Xiaopeng Cui, Wenlong Zhang, and Lin Qiao, 2016, Observational and dynamic downscaling analysis of a heavy rainfall event in Beijing, China during the 2008 Olympic Games, Atmospheric Science Letters, 17 (6): 368–376,DOI: 10.1002/asl.667. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asl.667/abstract
Huiqi Li, Xiaopeng Cui, Da-Lin Zhang, 2016, On the Initiation of an Isolated Heavy-Rain-Producing Storm near the Central Urban Area of Beijing Metropolitan Region, Mon. Wea. Rev., DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-16-0115.1, in press. http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/abs/10.1175/MWR-D-16-0115.1
Contact: CUI Xiaopeng, xpcui@mail.iap.ac.cn
