Scientists Develop a New Land Surface Model including Multiple Processes and Human Activities
Date:2020-12-17
Human activities, such as urban planning, irrigation and agricultural fertilization, affect terrestrial carbon, nitrogen and water cycle processes and aquatic ecosystems. Some human activities lead to water stress-- the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand-- and ecological environment damage, including groundwater lateral flow, and the movement of frost and thaw fronts. These changes in turn alter energy balance and water budget, and affect weather, climate and environment.
"We need a new land surface model to describe these processes," said Prof. XIE Zhenghui from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, "a comprehensive land surface model can not only provide a platform for water-energy simulations, but also contribute to water resources management, environment protection and sustainable development."
XIE and his team incorporated the schemes of groundwater lateral flow, human water use, soil freeze–thaw front dynamics, riverine nitrogen transport, and urban planning into a land surface model, and thus developed a land surface model CAS-LSM. According to XIE, the current version has improved the descriptions of biogeochemical process and urban modules, compared with the earlier version of this model.
"The new developed model can be applied to the simulation of inland river basins in arid areas to quantitatively evaluate the ecohydrological effects of stream water transfer,” XIE said. "Combined with basin simulation and climate system models, CAS-LSM can monitor river water environment. It can also help quantitatively evaluate weather and climate effects of South-to-North water transfer and provide advice for urban planning."
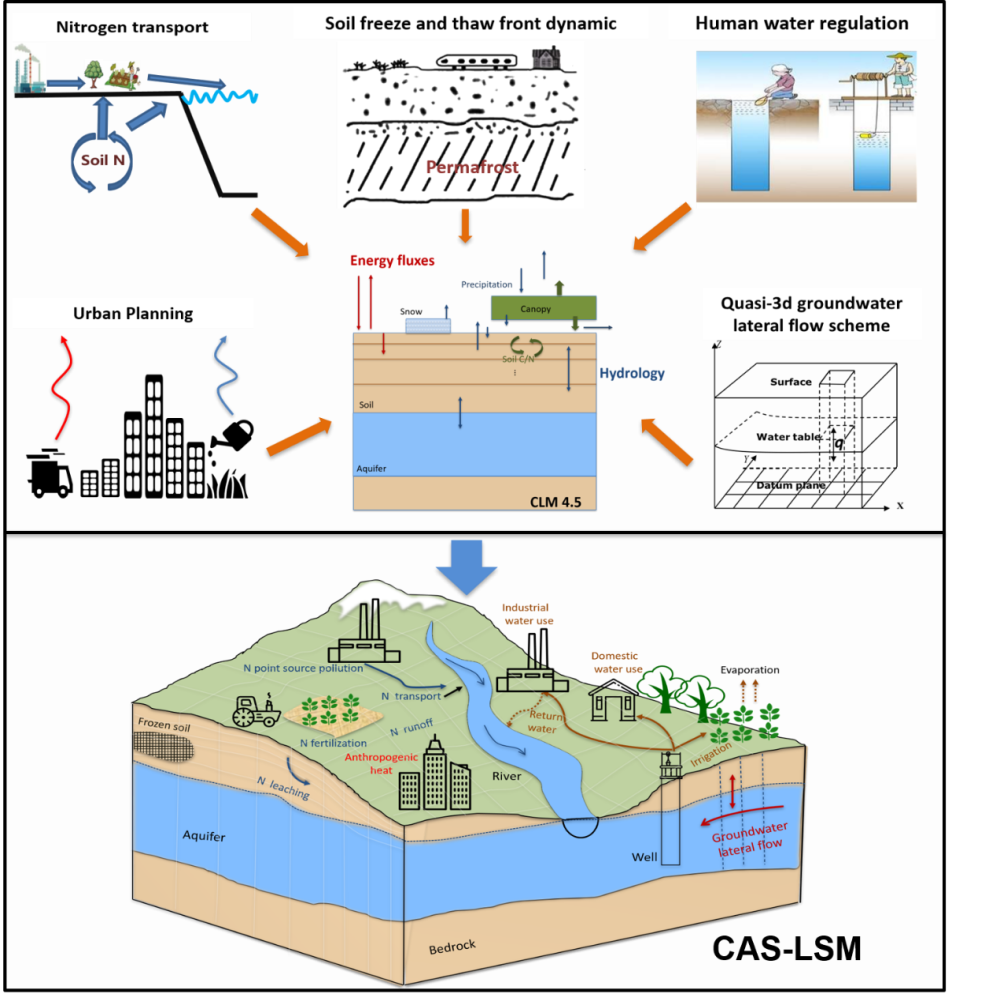
The primary processes considered in CAS-LSM, which were developed based on CLM4.5. (Image by WANG Longhuan)
This series of studies have been published in the special section "The Chinese Academy of Sciences Climate and Earth System Models (CAS-FGOALS and CAS-ESM) and Applications" in Journal of Geophysical Research- Atmosphere and Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems.
Citation:
1) Zhenghui Xie, Longhuan Wang, Yan Wang, Bin Liu, Ruichao Li, Jinbo Xie, Yujin Zeng, Shuang Liu, Junqiang Gao, Si Chen, Binghao Jia, Peihua Qin, Land surface model CAS‐LSM: Model description and evaluation, Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2020, 12, e2020MS002339. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002339 .
2) Longhuan Wang, Zhenghui Xie, Jinbo Xie, Yujin Zeng, Shuang Liu, Binghao Jia, Peihua Qin, Lijuan Li, Bin Wang, Yongqiang Yu, Li Dong, Yan Wang, Ruichao Li, Bin Liu, Si Chen. Implementation of groundwater lateral flow and human water regulation in CAS-FGOALS-g3. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2020, 125, e2019JD032289. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032289
Media contact: Ms. LIN Zheng, jennylin@mail.iap.ac.cn
