First Detection of NO3 Radicals in the Nocturnal Boundary Layer in China
Date:2021-03-17
In recent years, although the particulate matter concentration has notably decreased in China, the nitrate content in particulate matter has increased sharply, and the reason remains unclear. Nocturnal chemical reaction—the reaction that happens in the daytime—is the key factor driving nitrate evolution. However, NO3 radicals, as the main driving force of nocturnal chemical reaction, its vertical observation is nearly blank.
Dr. TANG Guiqian from the CAS Institute of Atmospheric Physics cooperated with Dr. WANG Shanshan from Fudan University and they set up a retroreflector at the 4-level of 325 m tower. Using Long Path Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy, the team observed the concentrations of NO3, O3 and NO2 simultaneously along the vertical direction for the first time in China.
"We found the production rate of NO3 at different heights is nearly constant," said TANG, "but the loss rate of NO3 in the upper nocturnal boundary layer is significantly lower than that near the ground due to the freshly emitted NO, which induces NO3 radicals accumulate in the upper nocturnal boundary layer and drives the nitrate formation in the boundary layer at night."
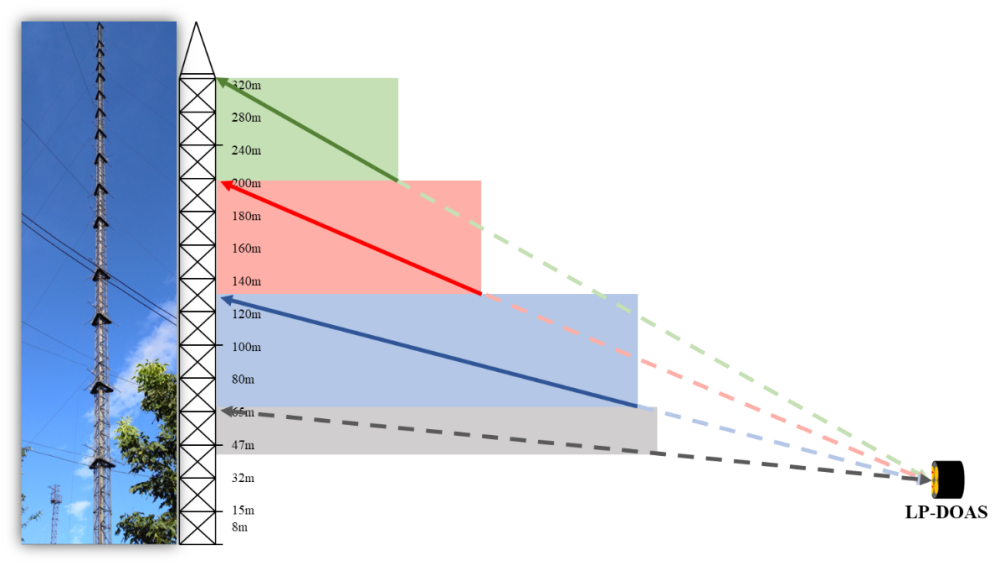
Detection of NO3 radicals during nocturnal boundary layer in Beijing. (Image by TANG Guiqian)
The study confirmed that the upper nocturnal boundary layer is the main area of nitrate formation, and TANG said the team's goal is to provide core technical support for the coordinated prevention and control of ozone and particulate matter in China.
The research results were published in Science of the Total Environment, and the study have been jointly funded by the national key R & D plan and the National Natural Science Foundation.
Reference
Yan, Y., Wang, S.*, Zhu, J., Guo, Y., Tang, G.*, Liu, B., An, X., Wang, Y., and Zhou, B.*, Vertically increased NO3 radical in the nocturnal boundary layer, Sci. Total Environ., 763, 142969, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142969, 2021.
