Aerosols are produced in large quantities during human activity and have a short life cycle. As a result, the significant pollution and climate effects of aerosol emissions are largely determined by where they occur.
Increasingly developed international trade has led to a separation between where products are produced and where they are consumed, leading to a large difference in pollution emissions associated with production and consumption in a region.
A collaborative research team led by Peking University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has quantified the impacts of consumption-related sulphate aerosols by developed and developing countries on global temperature and precipitation.
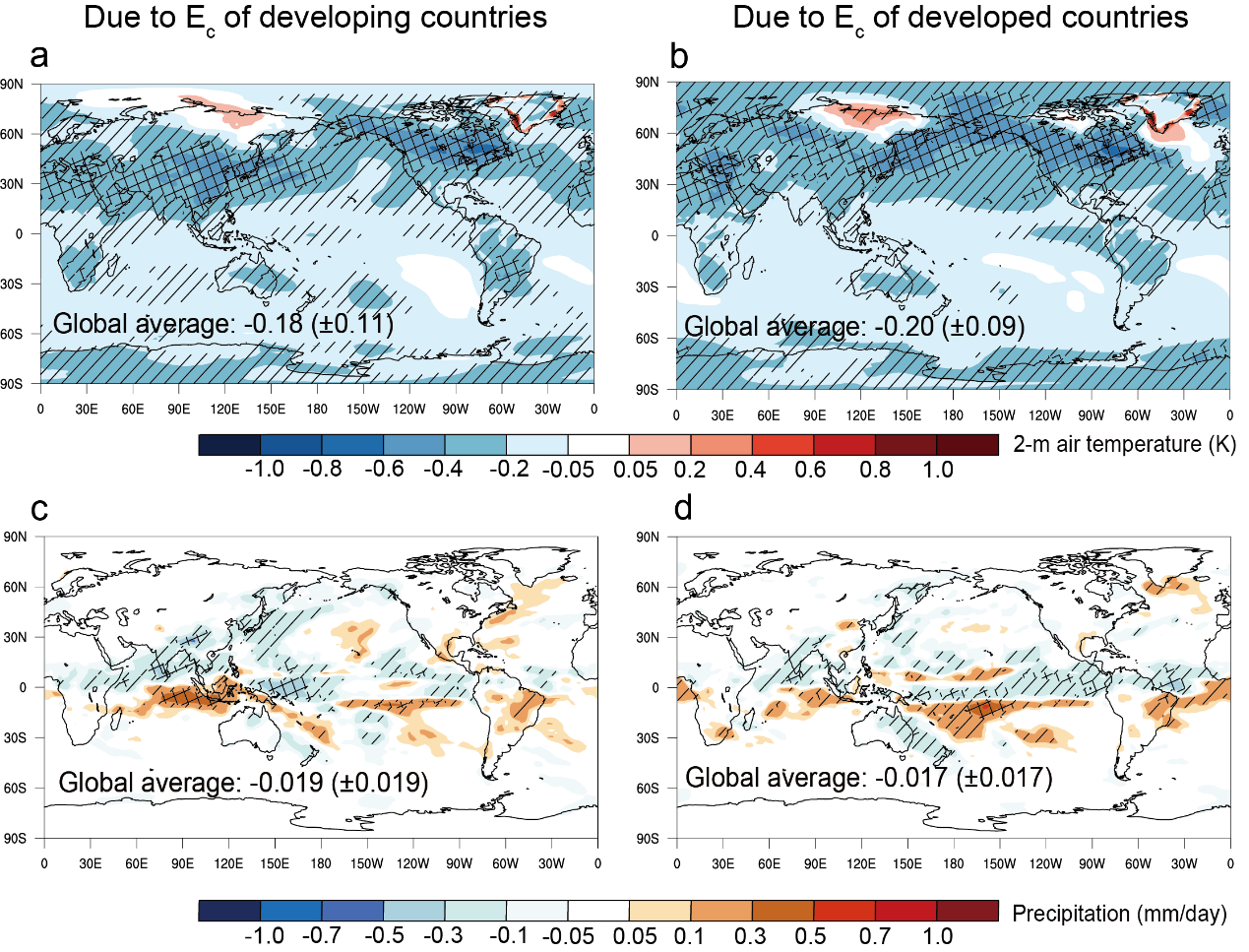
According to the team, although sulphur emissions associated with consumption activity in developed countries in 2014 were only 60% of those in developing countries, emissions from the two source regions had very similar effects on global mean near-surface air temperature and precipitation (about -0.2 °C and -0.02 mm/day).
"This is because the climate system is sensitive to forcing from both the magnitude and spatial pattern of aerosols," said first author LIN Jintai of Peking University.
Consumption-related sulphate by developing countries is concentrated at low and mid-latitudes in Asia, while consumption-related sulphate by developed countries is more evenly distributed zonally in the Northern Hemisphere and at higher latitudes overall. The effective radiative forcing and climate effects per unit of consumption-related sulphur emissions are stronger for developed countries.
Prof. Lin noted that studies on the extent of climate impacts by different regions "differ markedly" depending on whether a consumption perspective or a traditional production perspective is being used.
"Most of the past studies have focused on the aerosol climate effects caused by production activities, but in fact, consumption activities are just as important as production activities, and their impact remains unclear," said co-corresponding author HUANG Gang from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics of CAS.
Global temperature response (top) and precipitation response (bottom) to SO2 emissions associated with consumption in developing (left) and developed countries (right). (Image by Lin et al.)
Clarifying consumption-related emissions and their climate effects is therefore an important means of understanding the causes of climate change, promoting climate equity, and developing effective strategy for Climate Action and Responsible Consumption and Production, two of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals.
Citation: Jintai Lin, Chunjiang Zhou, Lulu Chen, Gang Huang, J.‐F. Lamarque, Ji Nie, Jun Yang, Kaiming Hu, Peng Liu, Jingxu Wang, Yan Xia, Yang Yang, Yongyun Hu: Sulfur emissions from consumption by developed and developing countries produce comparable climate impacts, Nature Geoscience, doi:10.1038/s41561-022-00898-2, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-022-00898-2 .
Media contact: Ms. LIN Zheng, jennylin@mail.iap.ac.cn