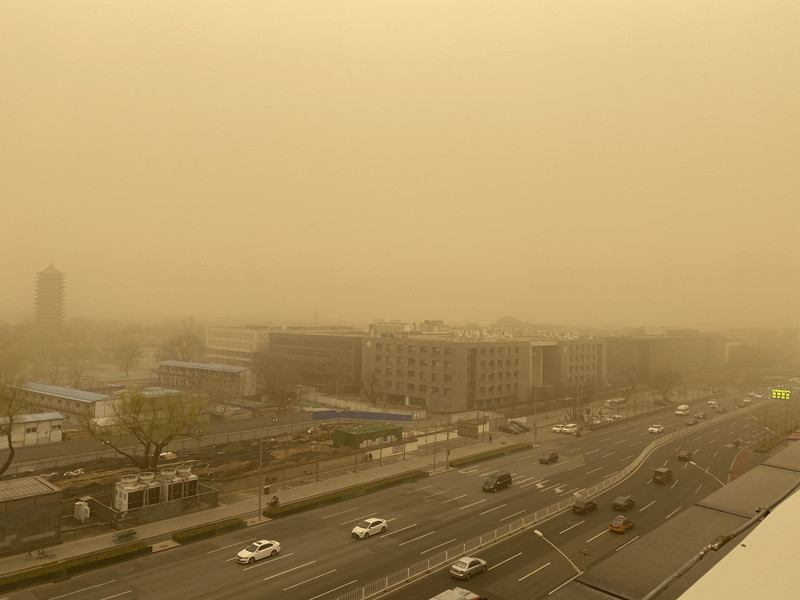
Extreme events such as the "North China Super Sandstorms" in March 2021 have significant impacts on human life, socio-economics and agricultural production (Figure 1). In addition to local meteorological conditions, sea surface temperature (SST) variability in different ocean basins also contributes to sandstorm frequency through atmospheric teleconnection and wave trains. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the impact of SST variability in these ocean basins on dust activities in North China.
Figure 1 The super sandstorm in North China on March 15, 2021 (Image by DONG Yueming)
To this end, the research group of Dr. LI Xichen, research scientist in the International Center for Climate and Environmental Sciences (ICCES), and Dr. LI Jing, associate professor in the School of Physics, Peking University, collaborated to study the variability in dust activity in the Gobi Desert and North China from 1981 to 2021, and in particular, to explore the relative contributions of SST variability in North Atlantic, Tropical Pacific and Sea Ice Concentration (SIC) in the Arctic to the spring dust activity in northeastern Asia. The research results were recently published online in Geophysical Research Letters.
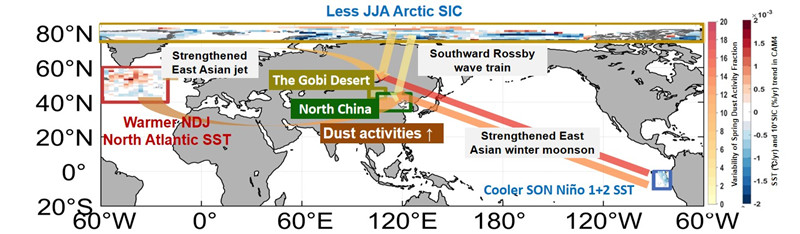
Figure 2 Variability of different ocean basins contribute to sandstorms in the Gobi Desert and North China. The color of the arrow: contribution of ocean variability to spring dust activity fraction in the Gobi Desert and North China. The color of the fill in the box: ensemble mean forcing trend of the Community Atmosphere Model version 4 (CAM4).
"Our study finds that positive North Atlantic SST anomalies, negative Tropical Pacific SST anomalies (analogous to La Nina), and anomalously low Arctic SIC in the previous summer can all contribute to dust generation in the Gobi Desert and its transport to north China by inducing more favorable local meteorological conditions." Said LI Jing. The above teleconnection patterns can be explained by established mechanism in atmospheric dynamics.
"Among the three ocean basins, the Tropical Pacific SST variability has the greatest impact on dust in the Gobi Desert, whereas the North Atlantic SST variability is the most important in driving dust events in North China. Considering the observed SST variability, the Tropical Pacific has the greatest impact on both regions." LI Xichen explained further.
They hope their study could provide theoretical support to better understand the causes of the variability of dust activity in northeastern Asia and to improve the modeling and projection of dust activities in this region.
Reference:
Liu, G., Li, J., Jiang, Z., & Li, X. (2022). Impact of sea surface temperature variability at different ocean basins on dust activities in the Gobi Desert and North China. Geophysical Research Letters, 49, e2022GL099821. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GL099821
Media contact: Ms. LIN Zheng, jennylin@mail.iap.ac.cn