Global Warming Intensifies Precipitation Extremes in China
Date:2021-01-11
Changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather and climate events have impacted human safety and the natural environment. Global warming increases holding capacity for atmospheric water vapor, therefore escalating water/energy circulation, which modifies the occurrence of precipitation extremes.

Torrential rainfall over Kanas Lake in Xinjiang, China (Credit: QIN Peihua)
Recently, Dr. QIN Peihua and his collaborators from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, investigated 21st century precipitation extremes in China using the regional climate model RegCM4 and global climate models (GCM). Both models participated in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5). Initially, the team assessed the performance of the CMIP5 and RegCM4 simulations of extreme precipitation for the current period (RF: 1982-2001). They found that CMIP5s and RCMs could capture the tempo-spatial variations in precipitation extremes. This work has been published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
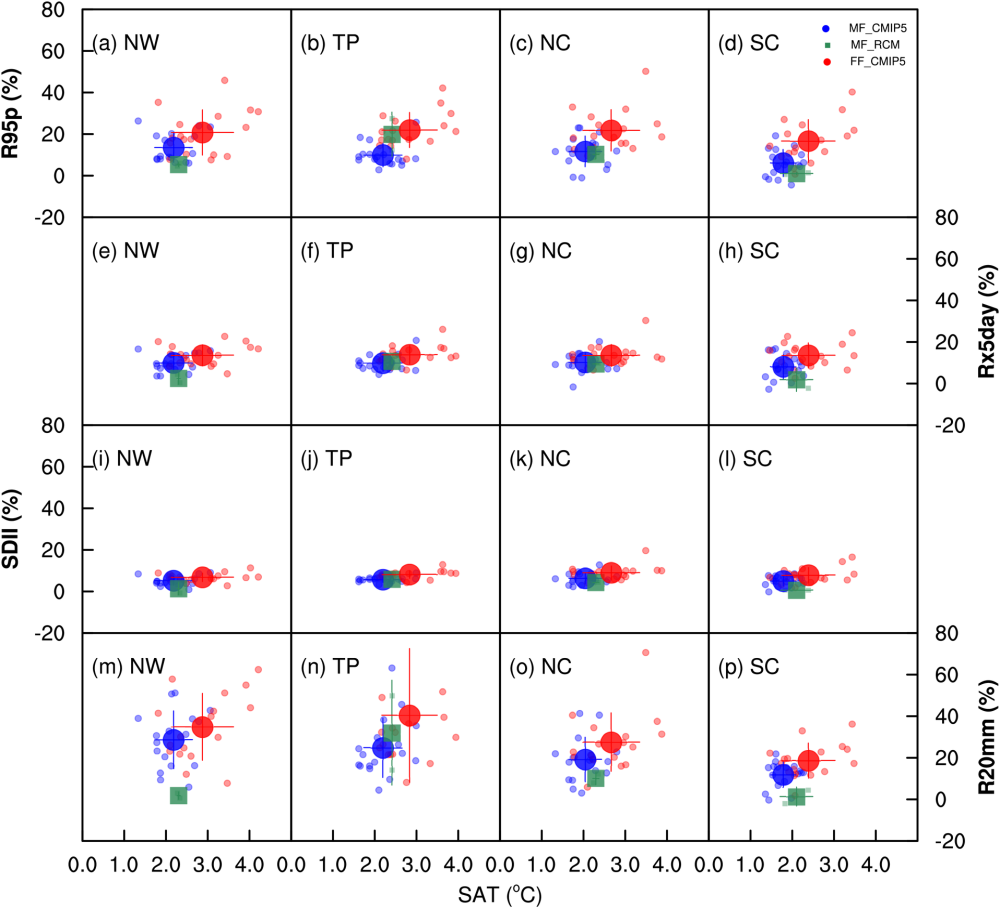
Changes in precipitation extremes over the four subregions in China during mid-future (blue: CMIP5, green: RegCM4) and far-future (red) under climate change. (Image by QIN Peihua)
QIN's study predcit that four subregions in China will see an increase of precipitation extremes within the mid-future (MF: 2039–2058) and far-future (FF: 2079–2098) relative to those for the RF period based on both CMIP5 ensemble mean and RCM ensemble mean. The ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) secular (non-seasonal) trends in the extremes are predicted to increase from 2008 to 2098. Furthermore, the research quantifies increasing rates of changes in precipitation extremes in the MF and FF periods in the four subregions of China with changes in air surface temperature.
"Finally, based on the water vapor equation, we find changes in precipitation extremes in China for the MF and FF periods have positive correlation with changes in the atmospheric vertical wind multiplied by changes in surface specific humidity." said QIN. "This finding might help understand and predict precipitation extremes better."
Reference: Qin, P. H., Z. H. Xie, J. Zou, S. Liu, S. Chen (2020). Future precipitation extremes in China under climate change and their physical quantification based on a regional climate model and CMIP5 model simulations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-020-0141-4
Media contact: Ms. LIN Zheng, jennylin@mail.iap.ac.cn
