|
|
 |
|
 |
|
Revisiting Mid-Holocene Temperature over China Using PMIP3 Simulations
Using the simulations performed by 15 climate models under the latest protocol of the Paleoclimate Modeling Intercomparison Project (PMIP) Phase 3 (PMIP3), the authors revisited the annual and seasonal temperature changes over China during the mid-Holocene. Similar to the previous results produced by PMIP Phase 1 (PMIP1) and 2 (PMIP2) models, 14 (15) of the 15 PMIP3 models reproduced colder annual (boreal winter and spring) temperature in response to mid-Holocene insolation changes, with an average cooling of 0.33 K (1.31 K and 1.58 K) over China. The mid-Holocene boreal summer (autumn) temperature increased in all (13) of the 15 PMIP3 models, with an average warming of 1.02 K (0.61 K) at the national scale. Those changes simulated by the PMIP3 models were similar to those from the PMIP2 simulations but generally weaker than those from the PMIP1 models. Similar to the previous PMIP1/2 simulations, a considerable mismatch still existed between the simulated cooling by the PMIP3 models and the reconstructed warming for annual and winter temperatures over China during the mid-Holocene, except over northern Northeast China, most of Xinjiang, and part of North and central China, where a slight warming was reproduced by most of the PMIP3 models. 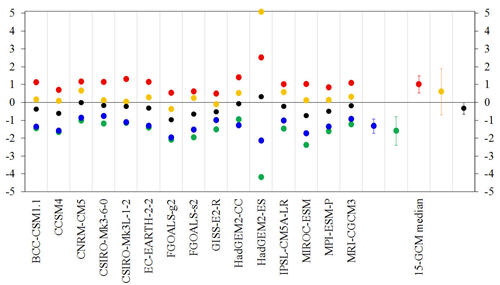
Figure 2 Mid-Holocene–baseline anomalies of regionally averaged annual (black), winter (blue), spring (green), summer (red), and autumn (orange) temperatures over China (units: K) obtained from the 15 models and their median, with plus/minus one standard deviation from the corresponding median expressed by the vertical bars.  Citation: Tian, Z.-P., and D.-B. Jiang, 2015: Revisiting mid-Holocene temperature over China using PMIP3 simulations, Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 8, doi:10.3878/AOSL20150040. Download: http://159.226.119.58/aosl/EN/abstract/abstract578.shtml |
|
|
|
