The Tibetan Plateau (TP), known as the third pole of the Earth, has a substantial impact on regional and global weather and climate. TP thermal effects vary at different time scales and have a significant influence on surrounding circulations, particularly during spring and summer. Due to rare observational records and inhomogeneous distribution of meteorological stations over TP, accurately estimating the intensity and change in TP thermal forcing remains a great challenge. Thus, a long and continuous dataset with more advanced parameterization scheme is required to support for research on the TP heating effect and a reliable reference for the evaluation of the quality of different reanalysis datasets.
Recently scientists in the State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid (LASG), the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences built a new dataset of atmospheric heat source/sink over TP, which might well satisfy this need.
By integrating the meteorological elements such as land surface temperature, air temperature, wind speed at 10 m, daily cumulative precipitation etc., scientists calculated and obtained the daily and monthly surface sensible heat flux and latent heat. The calculations are based on 6-h routine observations at 80 (32) Chinese meteorological Administration stations during the period 1979-2016 (1960-2016). Meanwhile, in situ air-column net radiation cooling during the period 1984-2015 was derived from satellite data.
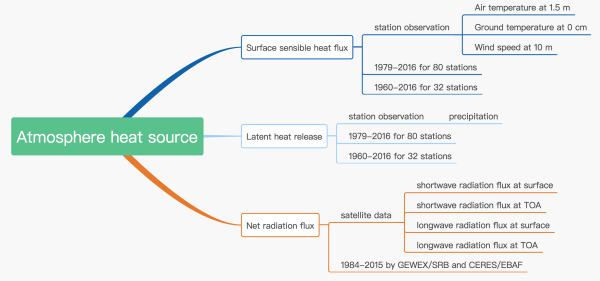
Diagram of dataset components and sources.
"This new dataset provides continuous, robust and the longest observational atmospheric heat source/sink data over the third pole, and will benefit a further understanding of the spatial-temporal structure and multi-scale variation in the TP diabatic heating and its influence on the earth’s climatic system” as introduced by the team leader Prof. DUAN Anmin.
The current data product was generated mainly based on GEWEX/SRB and CERES/EBAF satellite data. “We’ll continue to better the dataset in the future by using multi-source and multi-sensor satellite date, particularly including Chinese satellite datasets,” Prof. DUAN said.
This work has been published in Big Earth Data. And the
dataset can be downloaded from the website: http://staff.lasg.ac.cn/amduan/index/article/index/arid/11.html.
Citation: Duan, A., S. Liu, Y. Zhao, K. Gao and W. T. Hu, 2018: Atmospheric heat source/sink dataset over the Tibetan Plateau based on satellite and routine meteorological observations. Big Earth Data, 2, 179-189, DOI: 10.1080/20964471.2018.1514143.
